Multi-omic definition of metabolic obesity through adipose tissue–microbiome interactions
Article, Open Access, Nature Medicine, 2 January 2026
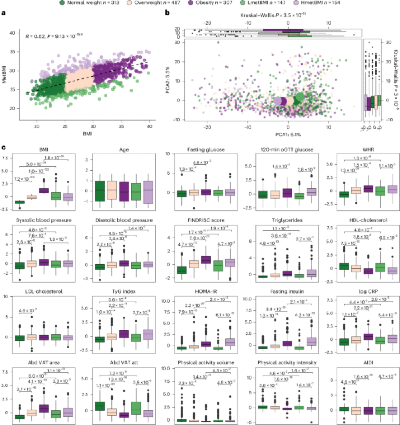
Obesity is now recognized as a chronic, multifactorial disease that drives dysfunction across the body and is a major cause of type 2 diabetes and cardiometabolic complications. Current diagnosis relies on BMI, which often fails to identify individuals at risk—up to 30% of people with T2D are not classified as obese by BMI. Multi-omics approaches, including metabolomics, offer a more precise view of metabolic health, revealing signatures linked to up to five-fold higher cardiovascular risk and strong interactions with gut microbiota. This study introduces a metabolome-informed BMI (metBMI) that better captures metabolic dysfunction, predicts treatment response, and highlights microbiome–metabolome pathways, paving the way for earlier and more personalized interventions beyond traditional BMI thresholds.